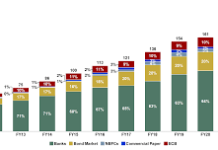
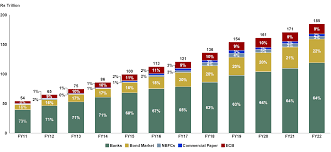
The COVID-19 pandemic revealed significant gaps in India’s healthcare system, but it also sparked innovations and collaborations that are now shaping the future of healthcare in the country. As India recovers from the immediate impact of the pandemic, its healthcare infrastructure is undergoing a major transformation. With continued investment, innovation, and policy reforms, the future of India’s healthcare system looks promising.
The Pandemic’s Impact on India’s Healthcare System
India’s healthcare system faced immense challenges during the pandemic. With a population of over 1.3 billion people, the demand for healthcare services far exceeded the available infrastructure.
Hospitals were overwhelmed, and access to essential services was limited, especially in rural areas. The healthcare workforce was stretched thin, and the existing public health infrastructure was tested in ways it had never been before.
The crisis also highlighted inefficiencies in resource allocation, supply chain issues, and the need for greater healthcare accessibility across urban and rural regions. These lessons have prompted the government and private sector to prioritize health system strengthening as part of the recovery process.
Post-Pandemic Recovery: Key Initiatives
India’s recovery efforts are being driven by multiple initiatives aimed at strengthening the healthcare system. FICCI Health Services Committee and NATHEALTH are leading the charge by advocating for increased investment in healthcare infrastructure, both public and private.
The Ayushman Bharat Scheme, which aims to provide affordable health insurance to over 100 million families, has expanded its coverage to ensure that healthcare access is available to more people, especially in rural and remote areas.
In addition to increased government funding, India is focusing on the digitalization of healthcare services. The National Digital Health Mission (NDHM) is facilitating the creation of a digital health ecosystem, enabling the secure sharing of health data and improving the delivery of telemedicine services.
The Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY) continues to be a key component in expanding coverage for low-income families, promoting equitable access to healthcare services.
Challenges to Overcome in Post-Pandemic Recovery
Despite these efforts, challenges remain. The pandemic underscored the importance of strengthening public health infrastructure and addressing health disparities between urban and rural areas. There is still a need for greater investment in medical equipment, staff training, and health system resilience.
The mental health crisis that has emerged in the wake of the pandemic also requires urgent attention, with an emphasis on psychosocial support and expanding access to mental health services.
Towards a Stronger and Smarter Healthcare System
India’s healthcare recovery will rely on public-private partnerships, government initiatives, and technological advancements. By integrating AI, telemedicine, and data analytics into the healthcare system, India has the opportunity to build a more resilient and efficient healthcare system that can withstand future crises.
The future growth of India’s healthcare sector is not only about increasing capacity but also about improving the quality of care and ensuring accessibility for all citizens. Industry bodies like FICCI Health Services Committee and NATHEALTH are playing a crucial role in shaping policies that drive healthcare reforms and ensure that the lessons from the pandemic result in long-term improvements.