Augmented Reality is rapidly becoming a transformative tool in various fields, with healthcare being no exception. From medical education to patient education, AR is providing new ways to enhance learning, improve training, and offer immersive experiences for patients and medical professionals alike.
As AR technology becomes more accessible, its role in healthcare is expanding, offering immense potential for improving both the quality of care and the effectiveness of medical training.
What is Augmented Reality?
Augmented Reality overlays digital information onto the real world, enhancing a person’s interaction with their environment. Unlike virtual reality (VR), which immerses users in a completely digital environment, AR works in conjunction with the real world, creating interactive and immersive experiences.
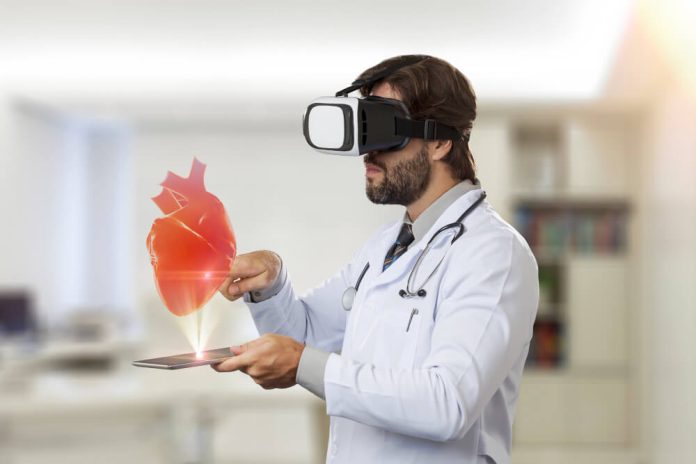
In healthcare, this technology is used to display vital patient data, assist in surgical procedures, or offer detailed 3D visualizations of anatomy during medical education and training.
Augmented Reality in Medical Education
One of the most exciting applications of AR in healthcare is in medical education. Traditionally, medical training has relied on cadavers, books, and two-dimensional images to teach students about human anatomy and surgical procedures.
With the advent of augmented reality, medical students now have access to interactive 3D models that allow them to study anatomy and practice surgical techniques in a more realistic and hands-on way.
Enhancing Surgical Training with Augmented Reality
AR technology has the potential to revolutionize surgical training by providing surgeons with a 3D overlay of the patient’s body, including virtual representations of organs, blood vessels, and bones. This immersive and accurate learning experience enhances the understanding of anatomy and organ positioning during surgery.
Moreover, AR in surgery is not only limited to training—it can also be used in real-time during procedures. Surgeons can access patient data, like CT scans or MRIs, overlaid directly onto the surgical site, helping guide them through complex procedures with greater precision and efficiency.
AR for Patient Education
Beyond medical education, AR is also transforming patient education by making complex medical concepts more accessible and easier to understand. For example, patients who are about to undergo a surgical procedure can use AR apps or tools to see a 3D model of their body, allowing them to better understand the area being operated on and the steps involved in their treatment.
Visualizing the Body’s Anatomy
Instead of relying on verbal explanations or flat illustrations, AR patient education tools allow patients to engage with interactive models of their body. These models can demonstrate how a specific medical condition or treatment will affect them, helping to reduce anxiety and improve understanding. Patients can see 3D images of their organs, bones, or tissues in real time, which fosters a deeper comprehension of their health condition.
Enhancing Treatment Compliance
With this technology, patients can visualize the effects of treatment or rehabilitation exercises. For example, an orthopedic patient could use an AR app to understand the steps involved in their recovery process, or a diabetic patient could learn how blood sugar levels impact their body using real-time data visualizations. This type of education can improve patient engagement, boost compliance with treatment plans, and ultimately lead to better health outcomes.
AR for Collaborative Learning and Communication
Another valuable aspect of AR in healthcare is its ability to foster collaborative learning and communication among medical professionals. During medical training, students and surgeons can interact with the same virtual models, allowing for shared learning experiences.
AR technology can also enable long-distance collaboration between experts from different locations, improving knowledge sharing and decision-making in real time.
For instance, a remote surgeon could guide a local surgeon through a complex procedure using AR-assisted visuals, providing step-by-step instructions and guidance overlaid onto the patient’s body. This type of real-time support can help improve outcomes and assist healthcare professionals in overcoming geographical barriers to expertise.
Benefits of AR in Medical Training and Patient Education
The integration of AR into medical education and patient education offers numerous advantages:
- Hands-On Learning: AR provides interactive learning experiences, allowing medical students and professionals to visualize, practice, and refine their skills without the need for cadavers or physical tools.
- Real-Time Feedback: With AR tools, trainees and surgeons can receive instant feedback during procedures, improving their skills and knowledge in a more immediate and effective way.
- Improved Patient Understanding: By providing patients with 3D visualizations of their condition or treatment, AR enhances their ability to comprehend medical concepts, which leads to better-informed and more engaged patients.
- Reduced Anxiety: Seeing a virtual representation of a procedure can alleviate patient fears and uncertainties. Understanding what is happening in their bodies, and how treatments work makes patients feel more confident and comfortable.
- Enhanced Collaboration: AR allows for shared learning experiences, bringing together medical professionals across different fields and locations to collaborate, share knowledge, and improve treatment outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations of AR in Healthcare
While augmented reality technology has immense potential, there are still challenges to overcome in its widespread adoption within healthcare:
- High Initial Cost: The development and deployment of AR systems in healthcare can be expensive. The technology itself, as well as the need for specialized hardware like AR glasses or headsets, can create a financial barrier for healthcare institutions.
- Technology Integration: Integrating AR systems into existing healthcare infrastructures, such as electronic health records (EHR) or imaging systems, can be complex and require significant investment in time and resources.
- User Adaptability: Medical professionals and patients must be trained to use AR systems effectively. Both doctors and patients may face a learning curve when adapting to new technologies.
- Privacy and Security Concerns: Since AR applications often rely on patient data, ensuring the privacy and security of this data is paramount. Healthcare providers must ensure that any AR systems comply with regulations like HIPAA to protect sensitive patient information.
The Future of AR in Healthcare
As AR technology continues to advance, its potential in healthcare will only grow. We can expect more intuitive and user-friendly AR tools that are easier to integrate into existing medical workflows. In the future, it could become a standard tool for medical professionals and patients alike, improving the quality of care, enhancing learning experiences, and offering new methods of educating patients about their health.
The evolution of augmented reality promises to be a game-changer in medical training and patient education. With the right investment and development, it could reshape the way we approach both healthcare education and patient care, providing deeper insights and more effective treatments for all.
I hope you find the above content helpful. For more such informative content, please visit Medtechreporter.