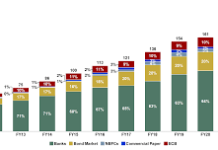
Telemedicine has rapidly become a cornerstone of India’s healthcare evolution, offering a solution to the country’s significant healthcare access challenges. With a population that is not only diverse but also geographically dispersed, especially in rural areas, telemedicine has the potential to bridge the gap between urban healthcare services and the underserved rural populations.
India’s healthcare system has traditionally struggled with providing timely and efficient services to people in remote areas. However, the surge in telehealth technologies is transforming the way healthcare is delivered, making it more accessible, affordable, and efficient for millions of Indians.
How Telemedicine Is Revolutionizing Healthcare Access
Telemedicine enables patients to consult healthcare providers remotely through digital platforms, whether it’s via video calls, phone consultations, or even text-based communication. For rural populations, this innovation has been a game-changer.
Patients in remote villages who previously had to travel long distances for basic healthcare services can now consult specialists from the comfort of their homes.
India’s telemedicine market has grown significantly, particularly post-pandemic, as the demand for remote consultations surged. The advent of digital health platforms, supported by the Indian government and private players, has made healthcare services more reachable for rural and semi-urban populations.
Mobile health apps, remote patient monitoring, and wearable devices are further enabling healthcare providers to track patient health in real time, reducing the need for in-person visits and improving outcomes.
The Role of Regulatory Bodies: NATHEALTH and FICCI
Industry bodies like NATHEALTH (Healthcare Federation of India) and FICCI have been instrumental in promoting the adoption of telemedicine across India.
These organizations work closely with the government to set clear regulatory guidelines and ensure that telemedicine practices comply with standards that ensure patient safety and confidentiality.
They have also been actively involved in advocating for the integration of telemedicine services into India’s broader healthcare strategy, encouraging the government to develop policies that foster the use of digital health technologies in both urban and rural areas.
The National Telemedicine Guidelines were introduced in 2020, making it easier for doctors to provide online consultations, improving regulatory clarity. By aligning their efforts with the government, these organizations are contributing significantly to the adoption of telehealth solutions that can tackle India’s healthcare access challenges.
Challenges to Overcome
While telemedicine presents huge potential, it comes with its own set of challenges. A significant concern is the digital divide, as many rural areas still face unreliable internet access and low-tech infrastructure. Additionally, the adoption of telehealth technologies requires digital literacy, which remains a hurdle in many regions.
There are also concerns around data security and patient confidentiality in remote consultations, which requires clear regulatory frameworks to ensure secure and trusted online healthcare interactions. Moreover, ensuring quality standards for telemedicine consultations is an ongoing challenge, and addressing these concerns will be critical to its long-term success.
The Future of Telemedicine in India
Looking ahead, the future of telemedicine in India is incredibly promising. With continued support from industry bodies like FICCI and NATHEALTH, India is poised to integrate telemedicine into its mainstream healthcare offerings.
There is great potential for telemedicine to not only reduce healthcare costs but also improve patient outcomes by providing timely interventions in areas that lack specialist services.
India’s path forward will involve scaling up digital infrastructure, improving internet access, and addressing regulatory and training gaps. As telemedicine continues to expand, it will likely become a vital component of India’s efforts to achieve universal health coverage and make healthcare accessible to every Indian citizen, no matter where they live.